Ransomware is Striking Everywhere Beware!
Ransomware is a significant problem which isn’t going away anytime soon. This article has tips on how to prevent an infection.
It is estimated Ransomware extorts over $10 million a year from businesses in the United States and even more abroad.
What is Ransomware?
Two of the most common forms of Ransomware are CryptoLocker and Cryptowall. These two forms of the malware operate very similarly. Both are forms of a Trojan horse. Once the Trojan horse is activated, it encrypts files on the compromised computer making them inaccessible. The perpetrators notify the victim(s) the files have been infected by displaying a screen which asks for a ransom. Sometimes the screen is direct and to the point:
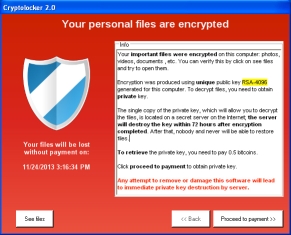
Ransomware Alert!
Other times the perpetrators use something a bit more creative like:

Either way, your files are encrypted and, basically, inaccessible.
What devices can become infected?
A Trojan horse malware is generally a type of malware which appears to be harmless. Once opened, the software goes to work causing theft of data, formatting of hard disk drives or in the case of Ransomware, encryption of the computer’s data.
While Trojan horse malware may be found on all kinds of devices, including Android Phones and Apple Products, these destructive software applications generally target the Microsoft Operating systems.
How does this malware spread?
The most common form of these products is spread through infected email. They are attached to email that may appear to come from a legitimate friend, contact or company. Another common method of distribution of malware is USB thumb or flash drives. Once the infected attachment or application is opened by the user, the malware is installed on the user’s computer system and goes to work.
The damage is done.
The Ransomware malware encrypts files stored locally on the computer system as well as on any mapped network drive it can see. This would include all mapped drives on networked servers a well as any locally connected flash drives and other external USB drives. The malware then encrypts your data in the background unbeknownst to you. After the files are encrypted, when the user attempts to open the files, the Ransomware displays a screen like those above and demands a payment.
While it is sometimes possible to decrypt the data many times it is not. If you pay the ransom it is hit and miss as to whether or not the files will be decrypted. In other words, there is no guarantee you will get your data back when you pay the ransom.
How to prevent Ransomware:
Social Engineering is frequently used to entice users to open attachments they otherwise wouldn’t open. Sometimes the sender of the email is familiar and the email encourages the recipient to “check out the great application” or “I am sending you this awesome photo of you”, when it isn’t even a photo.
There is no panacea for prevention of infection. The most effective way to prevent an infection is:
1) Educate users about the threat. Educate your employees, hold meetings, share this article, etc.
We cannot stress enough the need to educate users on the threats that are going to be thrown at them. Users should regularly be updated on the current threats and the prevention of those threats. Users who are used to installing anything they please on their computer are usually the biggest threat. The systems in use at Evidence Solutions, are locked down. Users cannot install software which is not approved.
User training should not only include computer security, but physical security and general security awareness training as well.
2) Install and use industrial grade antivirus / antimalware products. There are many on the market, consult with your IT department or IT professional to select the right one for you and your organization.
While standard security suites provide a good measure of protection, they are not infallible. New variants of Ransomware and other threats are cropping up daily.
There are also products on the market which help prevent the installation of malware. Products range in price from $15 per computer on up. One such product is CryptoPrevent. According to reviews it has been largely effective in preventing infection. This particular product creates a list of valid software which may be executed on the computer system. This “White List” prevents software not listed from being installed and executed. These types of products do require some configuration and maintenance. The invested time, however, can pay big dividends in the long run.
In addition, the Windows operating system can be configured to prevent unauthorized software from executing. While this is a “no software cost” solution it is effective but requires your IT department or professional to set it up. Products like CryptoPrevent, on the other hand, automatically update themselves.
CryptoPrevent has proven to be effective by disallowing the installation and execution of software unless it has been whitelisted. We now regard the risk of infection as high enough we believe this kind of precaution is warranted, even as we tell you no solution has been 100% effective.
Other security items firms should consider: Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS).
Recovery from a Ransomware infection:
The most common way to recover from a ransomware infection is to restore from backup. This should only be taken on after removal of the malware. This process is time consuming and expensive. One important thing to do is to make sure your backup system is properly designed to have multiple versions of your data. Restoring data which is already encrypted will not help.

